Delve into the intricate workings of the U.S. judicial branch with our icivics Judicial Branch in a Flash Answer Key. This comprehensive guide unravels the complexities of the court system, providing a clear and concise understanding of its structure, functions, and key principles.
From the Supreme Court’s pivotal role in shaping American jurisprudence to the diverse responsibilities of lower federal and state courts, this resource illuminates the essential elements of the judicial process, empowering readers to navigate the legal landscape with confidence.
Judicial Branch Overview
The judicial branch is one of the three branches of the US government. It is responsible for interpreting the law and resolving disputes. The judicial branch consists of the Supreme Court, lower federal courts, and state and local courts.
The judicial branch plays a vital role in the American system of government. It ensures that the laws are applied fairly and that the rights of individuals are protected. The judicial branch also helps to resolve disputes between states and between the federal government and the states.
Key Concepts
- Due process: The requirement that the government must follow fair procedures before depriving a person of life, liberty, or property.
- Equal protection: The requirement that the government must treat all people equally under the law.
Supreme Court Structure and Function: Icivics Judicial Branch In A Flash Answer Key
The Supreme Court is the highest court in the United States. It consists of nine justices who are appointed by the president and confirmed by the Senate. The justices serve for life, unless they resign, retire, or are impeached.
The Supreme Court has the power to interpret the Constitution and to strike down laws that it finds to be unconstitutional. The Court also has the power to review lower court decisions.
Landmark Supreme Court Cases
- Marbury v. Madison(1803): Established the principle of judicial review.
- Brown v. Board of Education(1954): Declared that racial segregation in public schools was unconstitutional.
- Roe v. Wade(1973): Legalized abortion.
Lower Federal Courts
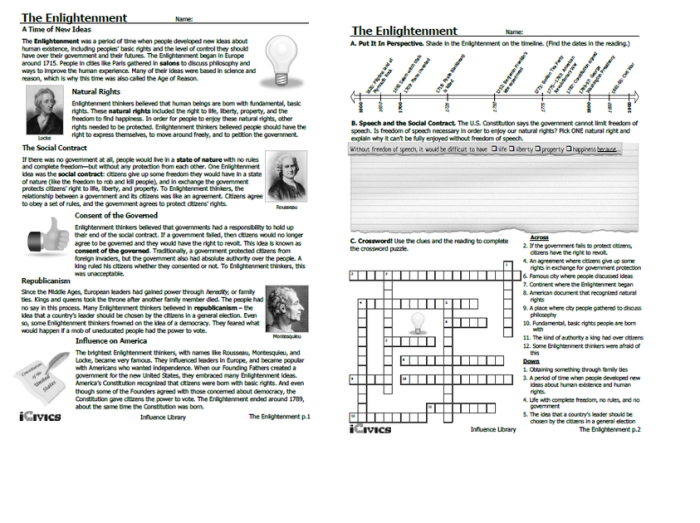
There are three levels of federal courts below the Supreme Court: district courts, courts of appeals, and specialized courts.
District courtsare the trial courts of the federal system. They hear cases involving federal law and diversity of citizenship.
Courts of appealsare the intermediate appellate courts of the federal system. They review decisions from district courts.
Specialized courtsinclude the Court of Federal Claims, the Court of International Trade, and the Tax Court.
Appealing Cases, Icivics judicial branch in a flash answer key
A party may appeal a decision from a district court to a court of appeals. A party may also appeal a decision from a court of appeals to the Supreme Court, but the Supreme Court only hears a small number of cases each year.
State and Local Courts
State and local courts are responsible for adjudicating the vast majority of cases in the United States.
State courtshave jurisdiction over cases involving state law. Local courts, such as city and county courts, have jurisdiction over cases involving local ordinances.
Role of State and Local Courts
State and local courts play an important role in interpreting and applying federal law. They also help to resolve disputes between individuals and businesses.
Key Principles and Concepts
Judicial Review
Judicial review is the power of the courts to interpret the Constitution and to strike down laws that they find to be unconstitutional. This power was established in the case of Marbury v. Madison (1803).
Precedent
Precedent is a legal principle that requires courts to follow the decisions of higher courts. This principle helps to ensure that the law is applied consistently.
Sources of Law
Judges rely on a variety of sources of law when making decisions, including the Constitution, statutes, and case law.
Current Issues and Challenges

Contemporary Debates
There are a number of contemporary debates surrounding the judicial branch, including the role of judicial activism, the appointment process for judges, and the impact of politics on the judiciary.
Challenges
The judiciary faces a number of challenges, including increasing caseloads and political polarization.
Potential Reforms
There are a number of potential reforms that could be implemented to address the challenges facing the judiciary, including increasing the number of judges, creating specialized courts, and reducing the number of cases that are appealed to higher courts.
Detailed FAQs
What is the primary function of the judicial branch?
The judicial branch interprets and applies the law, resolving disputes, protecting individual rights, and ensuring justice.
How many justices serve on the Supreme Court?
Nine justices serve on the Supreme Court, appointed by the President and confirmed by the Senate.
What is the process of judicial review?
Judicial review is the power of the courts to determine whether laws or government actions violate the Constitution.