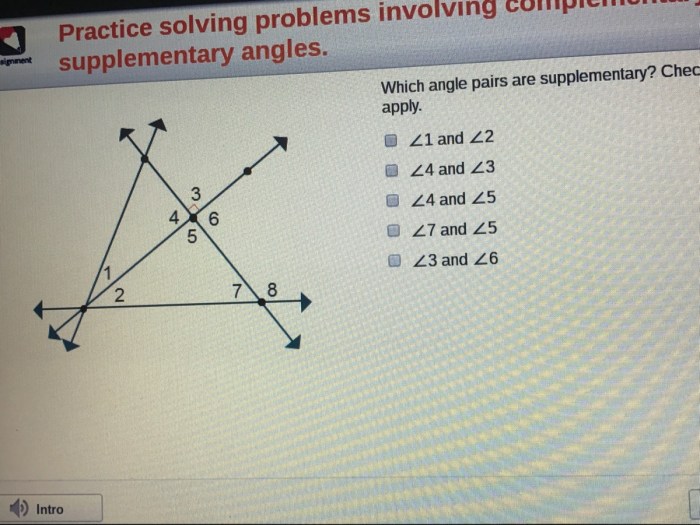
Use the diagram to identify the special angle pairs. – In geometry, understanding special angle pairs is crucial. This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of special angle pairs, their properties, and how to identify them in diagrams. By delving into the intricacies of supplementary, complementary, vertical, and adjacent angles, we can unlock their practical applications in various fields.
Special angle pairs possess unique relationships and properties that make them indispensable in solving problems and understanding geometric concepts. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and techniques to confidently identify and utilize these angle pairs in your mathematical endeavors.
Special Angle Pairs

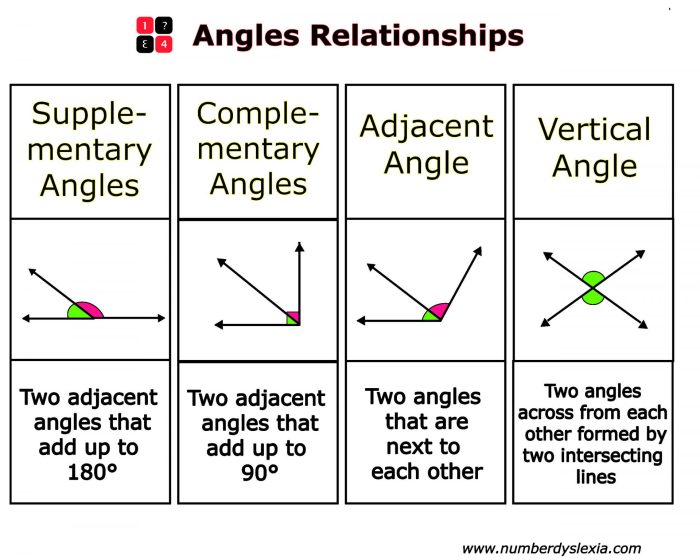
In geometry, special angle pairs refer to angles that have specific relationships with each other. These pairs are defined by their relative positions and the sum of their measures. The four main types of special angle pairs are supplementary, complementary, vertical, and adjacent angles.
These angle pairs are closely related to each other. Supplementary angles are adjacent angles that add up to 180 degrees. Complementary angles are adjacent angles that add up to 90 degrees. Vertical angles are opposite angles formed by two intersecting lines, and they are always congruent.
Identifying Special Angle Pairs in Diagrams, Use the diagram to identify the special angle pairs.
Identifying special angle pairs in diagrams is a crucial skill in geometry. Here are some tips for doing so:
- Supplementary angles:Look for angles that share a common side and are adjacent to each other. If the sum of their measures is 180 degrees, they are supplementary.
- Complementary angles:Similar to supplementary angles, complementary angles share a common side and are adjacent. However, the sum of their measures is 90 degrees.
- Vertical angles:Vertical angles are opposite angles formed by two intersecting lines. They are always congruent, meaning they have the same measure.
- Adjacent angles:Adjacent angles are angles that share a common vertex and a common side. They do not have to be supplementary or complementary.
Properties of Special Angle Pairs
Special angle pairs have specific properties that can be used to solve geometry problems. These properties include:
- Supplementary angles:The sum of the measures of supplementary angles is always 180 degrees.
- Complementary angles:The sum of the measures of complementary angles is always 90 degrees.
- Vertical angles:Vertical angles are always congruent, meaning they have the same measure.
- Adjacent angles:The sum of the measures of adjacent angles can be any value, depending on the angles’ individual measures.
Applications of Special Angle Pairs
Special angle pairs have numerous applications in real-world situations, including:
- Architecture:Architects use special angle pairs to design buildings, bridges, and other structures.
- Engineering:Engineers use special angle pairs to design machines, vehicles, and other mechanical systems.
- Design:Designers use special angle pairs to create aesthetically pleasing objects, such as furniture, clothing, and jewelry.
Creating a Reference Table
To summarize the information on special angle pairs, a reference table can be created:
| Type of Angle Pair | Definition | Properties | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplementary Angles | Adjacent angles that add up to 180 degrees | Sum of measures = 180 degrees | 90 degrees + 90 degrees |
| Complementary Angles | Adjacent angles that add up to 90 degrees | Sum of measures = 90 degrees | 30 degrees + 60 degrees |
| Vertical Angles | Opposite angles formed by two intersecting lines | Always congruent | 55 degrees and 55 degrees |
| Adjacent Angles | Angles that share a common vertex and a common side | Sum of measures can vary | 60 degrees and 30 degrees |
FAQ Resource: Use The Diagram To Identify The Special Angle Pairs.
What are special angle pairs?
Special angle pairs are pairs of angles that have specific relationships with each other, such as supplementary (summing to 180 degrees), complementary (summing to 90 degrees), vertical (opposite and equal), and adjacent (sharing a common side).
How do I identify special angle pairs in diagrams?
To identify special angle pairs in diagrams, look for angles that are adjacent, opposite, or sharing a common side. Use protractors or geometric tools to measure the angles and determine their relationships.