Practice kinetic and potential energy #2 delves into the captivating realm of energy, unveiling the intricate relationship between kinetic and potential energy. This exploration will illuminate their fundamental definitions, real-world manifestations, and practical applications, providing a comprehensive understanding of these vital energy forms.
Through engaging examples, interactive experiments, and insightful demonstrations, this discourse unravels the dynamic interplay between kinetic and potential energy, revealing their profound impact on our daily lives and the technological advancements that shape our world.
Kinetic and Potential Energy: Practice Kinetic And Potential Energy #2
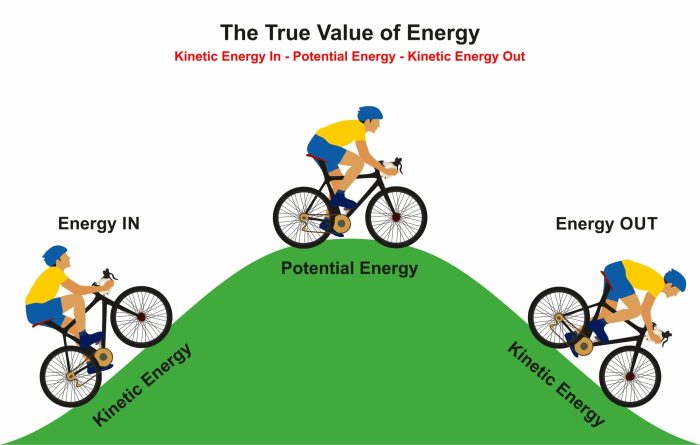
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion, while potential energy is the energy stored within an object due to its position or state.
The relationship between kinetic and potential energy is inverse. As an object’s kinetic energy increases, its potential energy decreases, and vice versa.
Examples of Kinetic and Potential Energy, Practice kinetic and potential energy #2
Kinetic energy examples:
- A moving car
- A rolling ball
- A spinning top
Potential energy examples:
- A rock sitting on a cliff
- A stretched rubber band
- A compressed spring
| Kinetic Energy | Potential Energy |
|---|---|
|
Depends on mass and velocity |
Depends on mass, height, or position |
|
Energy of motion |
Stored energy |
Applications of Kinetic and Potential Energy
Kinetic and potential energy are used in many everyday applications:
- Roller coasters use potential energy at the top of a hill to convert to kinetic energy as they descend.
- Pendulums use the conversion between kinetic and potential energy to keep swinging.
- Hydroelectric dams use the potential energy of water stored behind a dam to generate electricity.
Experiments and Demonstrations
Experiment to demonstrate the conversion of kinetic energy to potential energy:
Suspend a weight from a spring. Pull the weight down and release it. Observe how the weight rises to a height equal to the height from which it was dropped.
Demonstration to illustrate the relationship between kinetic and potential energy:
Roll a ball down a slope. Measure the ball’s velocity at the bottom of the slope and its height above the ground. Calculate the ball’s kinetic energy and potential energy at the bottom of the slope. The sum of the kinetic and potential energies should be equal to the ball’s initial potential energy at the top of the slope.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the difference between kinetic and potential energy?
Kinetic energy is the energy an object possesses due to its motion, while potential energy is the energy stored within an object due to its position or state.
How can kinetic energy be converted into potential energy?
Kinetic energy can be converted into potential energy by lifting an object against the force of gravity.
What are some examples of kinetic and potential energy in everyday life?
Examples of kinetic energy include a moving car, a flowing river, and a spinning top. Examples of potential energy include a raised book, a stretched rubber band, and a coiled spring.